Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is an essential aspect of any business, as it helps companies build and maintain strong relationships with their customers. It involves managing interactions with customers throughout the entire customer lifecycle, from the initial contact to post-sales support. In this article, we will explore some examples and uses of CRM, as well as the four key components of the CRM process.
Customer Relationship Management Examples + Uses
CRM is widely used across various industries and sectors to improve customer satisfaction, increase sales, and streamline business processes. Let’s take a look at some examples and uses of CRM:
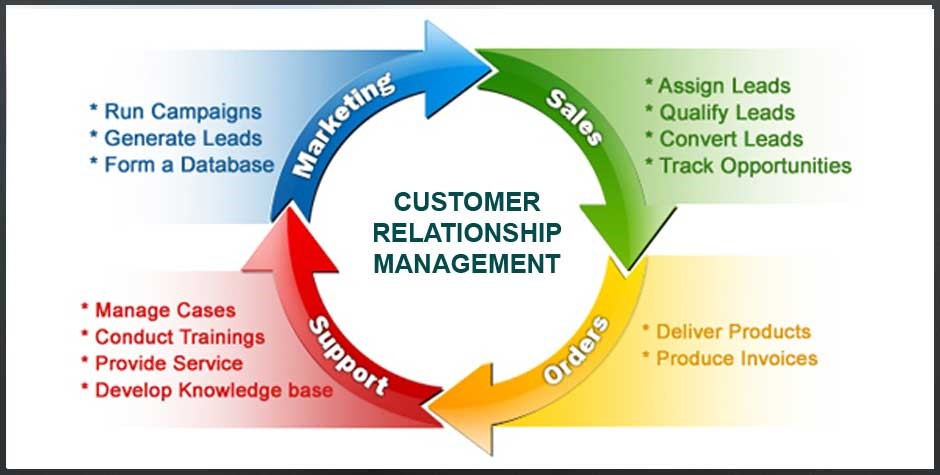
1. Sales Management: CRM systems are often used to manage sales pipelines, track leads, and facilitate effective sales processes. By having a centralized platform for managing customer information and sales activities, companies can enhance their sales performance and improve overall revenue.
2. Customer Support: CRM tools can also be used to provide efficient customer support. By storing relevant customer data in a CRM system, support agents can quickly access information about customers’ previous interactions, preferences, and issues. This enables them to provide personalized and prompt assistance, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
3. Marketing Campaigns: CRM systems help businesses create targeted marketing campaigns by segmenting customers based on their preferences, purchase history, and behavior. By leveraging this data, companies can tailor their marketing messages and promotions to specific customer segments, resulting in higher engagement and conversion rates.
4. Customer Analytics: CRM platforms provide valuable insights into customer behavior and trends. By analyzing customer data, companies can identify patterns, preferences, and opportunities for upselling or cross-selling. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions, improve customer experience, and drive profitability.
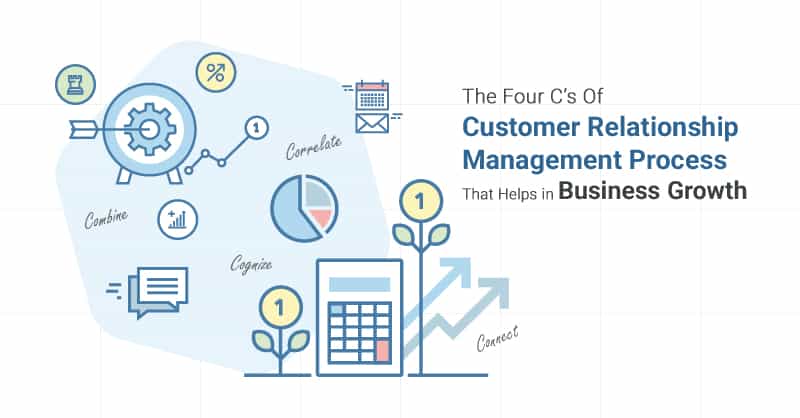
The Four C’s of Customer Relationship Management Process
The CRM process consists of four key components, also known as the Four C’s:
1. Collaboration: Collaboration is an essential aspect of CRM, as it involves fostering teamwork and communication among different departments within an organization. By promoting collaboration, companies can ensure that every team member has access to accurate and up-to-date customer information, enabling them to deliver consistent and personalized experiences.
2. Communication: Effective communication is crucial in CRM, both internally and externally. Internally, teams need to communicate regularly to ensure that customer information is updated, issues are resolved promptly, and knowledge is shared. Externally, businesses must maintain open lines of communication with their customers through various channels, such as emails, social media, and chatbots.
3. Customer Data: The collection and analysis of customer data form the foundation of CRM. Businesses need to gather relevant customer data, such as contact information, purchase history, and preferences. By organizing and analyzing this data, companies can gain insights into customer behavior, trends, and needs, enabling them to tailor their offerings and interactions accordingly.
4. Customer Experience: Ultimately, the goal of CRM is to deliver exceptional customer experiences. By leveraging customer data, businesses can provide personalized interactions, anticipate needs, and resolve issues quickly. A positive customer experience leads to increased loyalty, repeat purchases, and positive word-of-mouth, which are crucial for long-term business success.
Conclusion
Customer Relationship Management plays a vital role in the success of businesses across industries. By implementing CRM systems and strategies, companies can improve sales, enhance customer support, and optimize marketing efforts. The Four C’s of the CRM process – collaboration, communication, customer data, and customer experience – provide a framework for effective CRM implementation. By prioritizing these components, businesses can cultivate strong relationships with their customers and drive sustainable growth.
In conclusion, CRM is not just a technology or a strategy; it’s a mindset that puts the customer at the center of a business’s operations. By focusing on building and nurturing relationships with customers, businesses can thrive in today’s competitive marketplace.
Are you looking for Using Customer Relationship Management to Your Advantage? you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Images about Using Customer Relationship Management to Your Advantage like Customer Relationship Management Examples + Uses, Using Customer Relationship Management to Your Advantage and also Using Customer Relationship Management to Your Advantage. You can read more here:
Using Customer Relationship Management To Your Advantage

stitchcraftmarketing.com
Firms is a crucial component of the global economy. Business owners exploit opportunities to establish successful ventures that add economic growth and employment.
7 Tips To Maximise Your Marketing Funnel – Grow

wearegrow.com
Entrepreneurs is a crucial component of the global economy. Innovators utilize opportunities to establish successful ventures that add economic growth and job creation.
Customer Relationship Management Examples + Uses

crm.walkme.com
Firms is a vital factor of the international economy. Entrepreneurs leverage opportunities to develop lucrative ventures that contribute economic growth and job creation.
The Four C’s Of Customer Relationship Management Process
www.convergehub.com
Business is a crucial aspect of the worldwide economy. Entrepreneurs leverage opportunities to create successful ventures that contribute to economic growth and employment.
Customer Relationship Management
studylib.net
Business is a essential component of the worldwide economy. Innovators leverage opportunities to create profitable ventures that contribute to economic growth and employment.
In the digital age, technology plays a essential role in business operations. Companies embrace cutting-edge resources and software to streamline processes, improve communication, and maximize performance. Data analytics enables decision-making, while e-commerce systems ease online transactions and global reach.